Eye Tracking as a Cost-Effective Tool in Neuroscience Research
Almost all animals with functional vision exhibit a variety of eye movements. These movements allow compensation for shifts in the visual scene and enable tracking
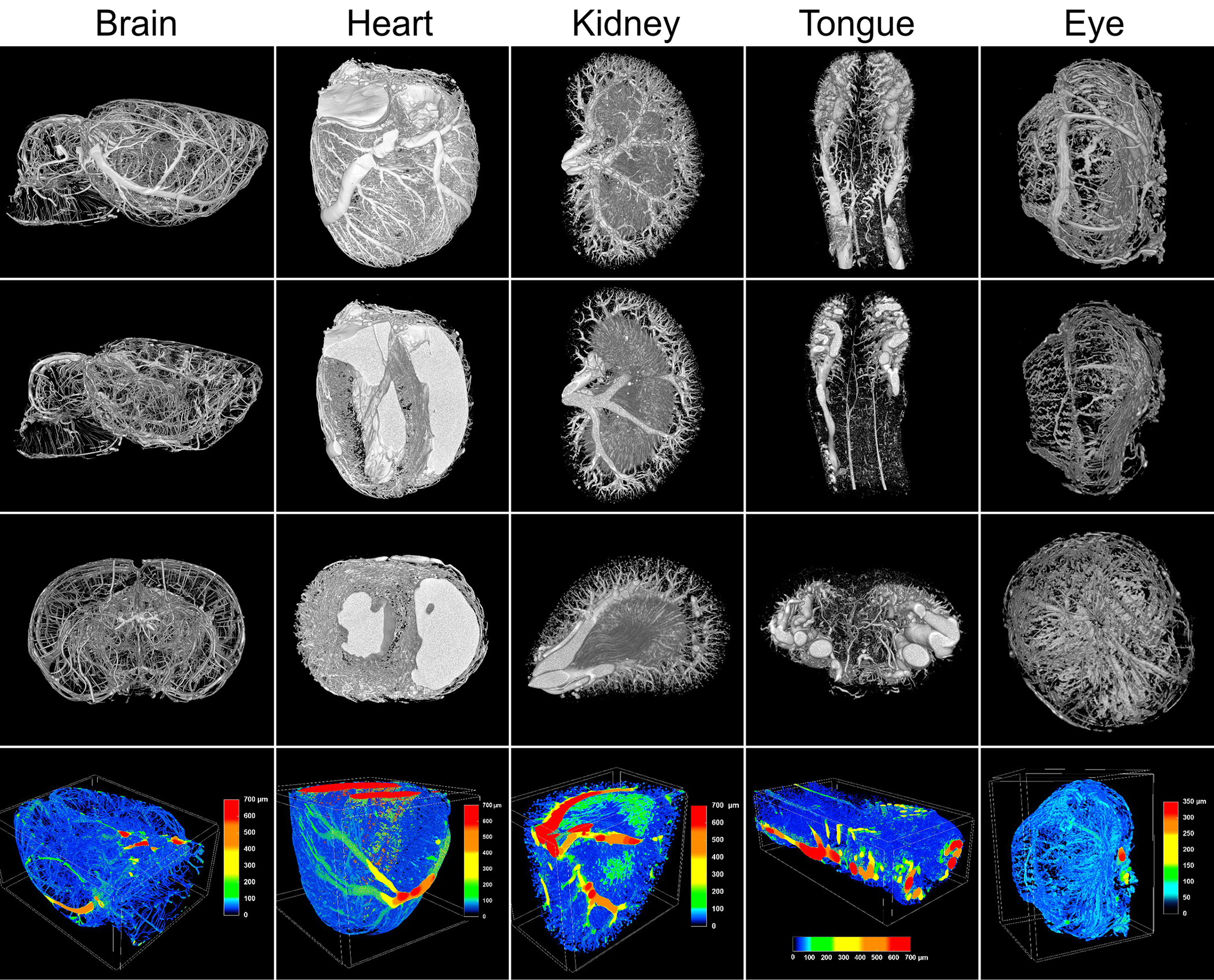
Recent advancements in high-resolution micro CT imaging have opened new doors for researchers, enabling them to explore microvascular structures in unprecedented detail.
Micro CT (computed tomography) is a powerful imaging technique that allows for the non-invasive visualization of internal structures at high resolution. This technology has gained prominence in studying vascular systems due to its ability to capture the fine details of blood vessels, making it an invaluable tool for researchers focused on organ interactions and disease mechanisms.
A recent study with Vascupaint has introduced a new perfusion protocol tailored for high-resolution micro CT imaging, emphasizing its effectiveness in visualizing vascular networks across multiple organs in rats which has the potential of aiding research into various pathological conditions.
The study introduced the concept of “vascular fingerprints,” which refers to the unique distribution of vascular volume based on vessel diameters. This innovative concept has the potential to serve as a diagnostic tool, aiding in the identification of pathological changes across different organ types. The research highlights several significant advancements in micro CT imaging protocolsThe study employed a “highest resolution” protocol, which successfully visualized blood vessels with diameters as small as 20-25 μm. This level of detail is critical for accurately assessing vascular health and detecting abnormalities.
The researchers evaluated three imaging protocols—highest resolution, intermediate settings, and fastest scanning. Notably, the intermediate settings provided results nearly equivalent to the highest resolution while improving efficiency, demonstrating a practical balance for researchers utilizing micro CT products.
The multi-organ perfusion protocol demonstrated high reproducibility, with low standard deviations in vessel diameter measurements across subjects. This reliability is crucial for quantitative data analysis, enabling researchers to draw meaningful conclusions from their findings.
The methodological advancements detailed in this study represent a significant leap forward in the field of micro CT imaging. By providing a reliable and efficient means of visualizing microvascular networks, these innovations enhance our ability to investigate the roles of vascular structures in various diseases, including cardiovascular disorders, diabetes, and cancer.
Researchers using Vascupaint can leverage these findings to deepen their understanding of microvascular alterations and their implications for organ health. Moreover, the ability to analyze multiple organs in a single study presents new opportunities for exploring systemic interactions and disease mechanisms.
Napieczyńska H, Kedziora SM, Haase N, Müller DN, Heuser A, Dechend R, Kräker K. μCT imaging of a multi-organ vascular fingerprint in rats. PLoS One. 2024 Oct 14;19(10):e0308601. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308601. PMID: 39401231; PMCID: PMC11472947.
Almost all animals with functional vision exhibit a variety of eye movements. These movements allow compensation for shifts in the visual scene and enable tracking

Medilumine is pleased to announce a new distribution partnership with NanoPET Pharma through its Viscover brand. Medilumine is now an authorized distributor of the full